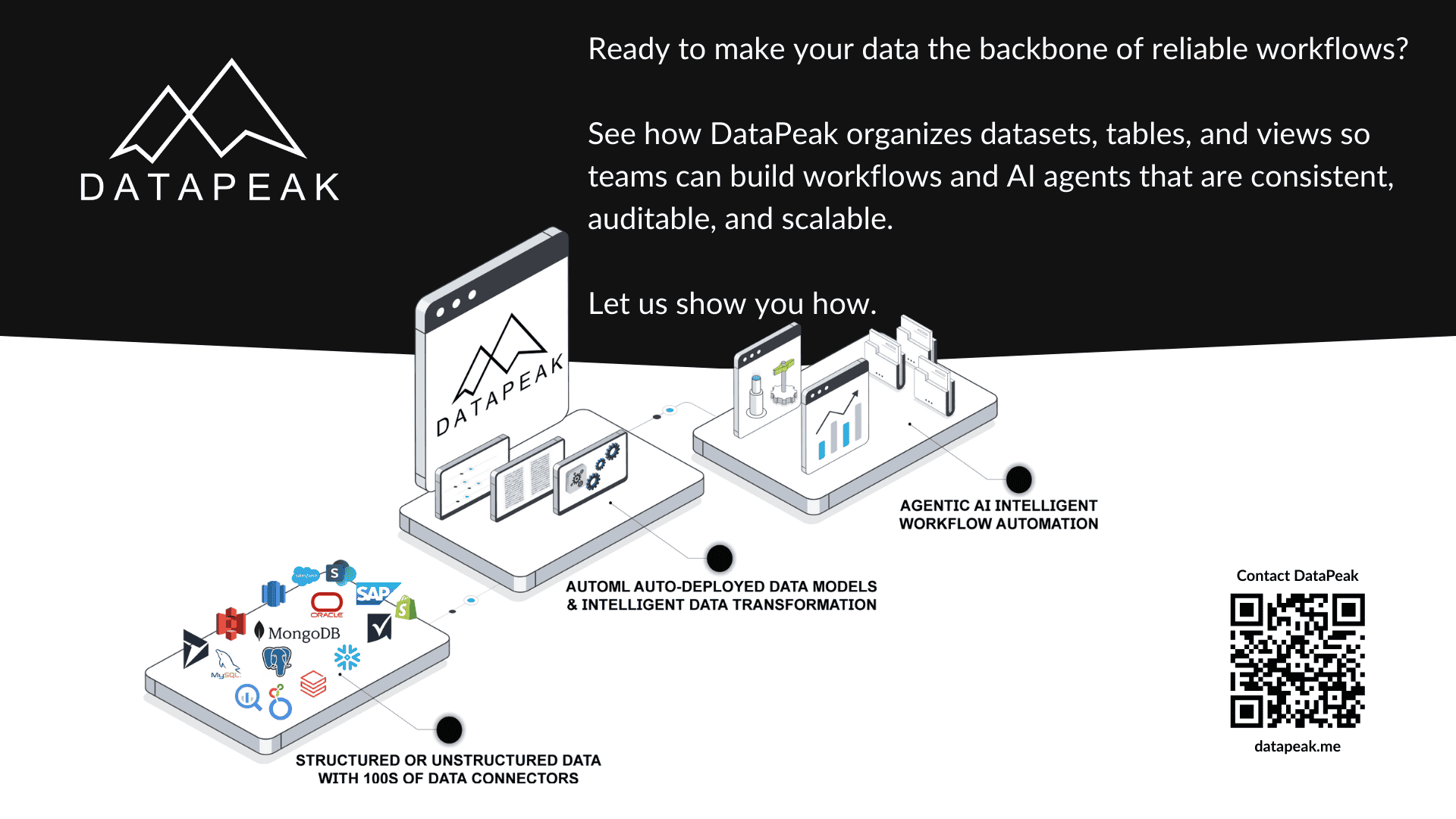
How Data Is Organized in DataPeak: Datasets, Tables & Views
When data systems fail, it’s rarely because of a single bad decision. More often, it’s because structure was added too late, after workflows, automations, and integrations were already in motion.
DataPeak was designed to avoid that trap.
Instead of treating data as something workflows consume passively, DataPeak treats data as a first-class component of the system. Everything, workflows, agents, and outputs, is built on top of a clear data model.
This article explains how data is organized in DataPeak using datasets, tables, and views, and why that structure matters.
Why Data Structure Matters More Than Tools
Modern teams use countless tools to collect and process data. What’s often missing is a shared structure that makes data understandable and reliable across systems.
Without structure:
Workflows become brittle
AI agents lack context
Errors propagate silently
Trust in outputs erodes
DataPeak’s approach focuses on making data explicit before it’s used anywhere else.
Datasets: The Container for Related Information
In DataPeak, a dataset is a logical grouping of related data.
A dataset might represent:
Orders
Inventory
Documents
Assets
Transactions
Operational records
Datasets provide:
A single source of truth
Clear ownership
Controlled access
Consistent structure
By organizing information into datasets, DataPeak ensures that workflows and agents always know what data they’re working with.
Tables: Structure Within the Dataset
Within each dataset, data is stored in tables.
Tables define:
Fields and data types
Relationships between records
Validation rules
Update behavior
This structure allows DataPeak to:
Enforce consistency
Reduce ambiguity
Support reliable automation
Enable scalable AI use
For teams coming from spreadsheets or databases, tables provide a familiar but governed environment.
Views: Context Without Duplication
Views allow teams to look at the same data in different ways without duplicating it.
A view might:
Filter records
Combine fields
Present data for a specific workflow
Support a particular role or task
Views are especially valuable when:
Multiple teams use the same dataset
Workflows require different subsets of data
Permissions vary by role
By using views instead of copies, DataPeak maintains consistency while supporting flexibility.
How Datasets Support Workflows
Workflows in DataPeak don’t pull data from arbitrary sources, they operate on defined datasets and tables.
This ensures:
Inputs are predictable
Logic is repeatable
Outputs are traceable
When data changes, workflows respond in controlled ways rather than breaking unexpectedly.
How Datasets Support AI Agents
AI agents rely on context to make decisions.
Because DataPeak datasets are structured and governed, agents can:
Evaluate data confidently
Understand relationships
Apply logic consistently
Avoid hallucinations caused by ambiguity
This dramatically improves decision quality compared to unstructured AI integrations.
Governance Without Friction
DataPeak’s data model supports governance without slowing teams down.
Key features include:
Clear permissions
Controlled updates
Auditability
Visibility into data changes
This makes DataPeak suitable for environments where compliance and accountability matter.
Evolving Data Without Breaking Workflows
One of the biggest challenges in data systems is change.
DataPeak allows datasets to evolve while maintaining stability by:
Managing schema updates carefully
Preserving relationships
Allowing workflows to adapt incrementally
This reduces the risk of cascading failures as systems grow.
Why This Matters for AI Adoption
AI systems are only as trustworthy as the data they rely on.
By structuring data explicitly, DataPeak ensures that:
Agents operate on reliable inputs
Decisions are explainable
Outputs can be validated
This is essential for responsible AI use in business environments.
Data organization is not glamorous, but it’s foundational. By structuring data through datasets, tables, and views, DataPeak creates an environment where workflows and AI agents can operate reliably, transparently, and at scale. That structure is what turns automation into infrastructure.